
When deciding which resource type to use, it is essential to consider the organization’s specific needs. For example, if an organization is a software company and its activities involve developing software, assigning costs based on hours worked rather than users would be better. As a result, the activity-based approach leverages activities rather than functional divisions (also known as Cost Centers) to absorb overhead costs. One of the most fundamental characteristics of functional departments is the tendency for such departments to include various activities that might result in various expenses and behave in various ways. The first step in activity-based costing involves identifying activities and classifying them according to the cost hierarchy. Cost hierarchy is a framework that classifies activities based the ease at which they are traceable to a product.

What challenges need to be considered when implementing activity-based costing?
Low-level participation activities, such as accounting and marketing, have less impact on product creation and often require fewer resources. For example, if a company can identify the resources consumed by developing or marketing the product, it can compare its actual results with expected outcomes. It helps them track progress and make necessary changes to ensure that activities run efficiently. As an activity-based costing example, consider Company ABC, which has a \$50,000 per year electricity bill. The cost driver in this illustration is the 2,500 total hours of labor that were put in during the year.
How does activity-based costing compare to other cost allocation methods?
The internet, catalogs, retail stores, and distributors are typically some of the distribution and sales channels businesses use today. When you analyze a project, you should find out how much it will cost to complete. You should change your plans to avoid paying so much if it is too high. You can QuickBooks save money if you hire the right professionals for the job. Incentive alignment is when rewards are structured so that they are based on ABC information rather than on traditional ways.
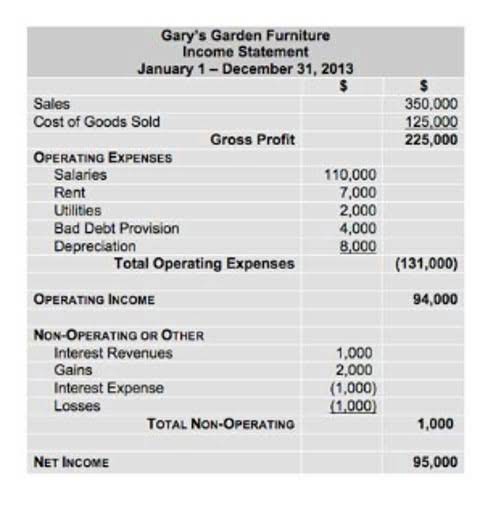
Process Costing

Activity-Based Costing (ABC) differs from traditional costing by focusing on activities as the primary cost drivers rather than allocating overhead costs broadly. ABC provides a more accurate and detailed view of resource consumption, leading to better decision-making and cost control. To break it down, you first calculate the cost per unit of each activity by dividing the total overhead costs by the total cost of driver units. Then, this rate can be applied to the units consumed Accounting For Architects by a specific product or service. Knowing how to calculate activity-based costing helps businesses precisely track expenses.
FAQ: The ABCs of Activity Based Costing
It assumes the activity will consume resources and will generate results. By determining the resources, activities, expenses, and quantities necessary to generate output using the ABC method, overhead costs may be linked to the products and services produced. When calculating the cost of each action carried out over a specific amount of time, a unit or output (also known abc costing example as a driver) is required. Traditional costing spreads costs across products and services using rough estimates, like labor hours or machine time. These old methods hide the real cost drivers, leading to mispricing, wasted resources, and lost profits. ABC has been shown to provide more accurate product costs than traditional costing methods and can help managers make better pricing decisions, product mix, and resource allocation.
- The ABC system breaks down manufacturing overhead into cost pools such as machines, raw materials, salaries, utilities and anything else that costs money.
- ABC is a subfield of managerial accounting concerned with allocating an activity’s indirect costs, also known as overheads.
- Once these activities have been identified, managers must assign cost drivers and allocate resources accordingly.
- Even Robert Kaplan, a professor at Harvard Business School who is frequently regarded as the founding father of the concept, has recognized that it reached a plateau in the 1990s.
- An activity cost pool is a temporary account considering fixed and variable costs.
Time-Consuming Data Collection
Even secure timesheets can help stay on budget by tracking labor costs. That’s because there are static documents that must be manually updated. Use project management software for more effective cost management. ProjectManager is award-winning project and portfolio management software that has multiple activity planning, schedule and tracking tools to plan, manage and monitor costs in real time.
- As a result, the activity-based approach leverages activities rather than functional divisions (also known as Cost Centers) to absorb overhead costs.
- Activity-based costing can be a helpful tool for improving cost management.
- When you finish your Cost-Benefit Analysis, you will know how profitable the business project is.
- ABC costing is mostly used by manufacturing businesses, but other complex business types or service-based companies can also benefit.
Standard costing uses predetermined costs for materials, labor, and overhead. Businesses compare these standards to actual costs to see if they are over or under budget. Job order costing is used by businesses that make custom products. This helps with better pricing, smarter budgeting, and cost control. What do you like about it over the more simplified traditional methods? Would you recommend others in manufacturing industries make the switch?

For simplicity, let’s assume that the remaining $1,800,000 of manufacturing overhead is caused by the production activities that correlate with the company’s 100,000 machine hours. Activity-based costing calculates overhead (indirect expenses) costs by taking multiple cost drivers (machine setup costs, labor, inspections, utilities, etc.) into account before assigning product costs. Activity-based costing is an incredibly precise method used by large companies needing accurate figures when allocating overhead costs. The final step is to use the data from the ABC technique to take actions to minimize costs and maximize profits. For example, a company might decide to streamline a high-cost activity, eliminate inefficiencies or adjust prices to reflect the true cost of production. These levels include batch-level activity, unit-level activity, customer-level activity, organization-sustaining activity, and product-level activity.

